Gamification
Gamification is the use of game design techniques and game elements to solve non-game problems. The goal is to tap into the psychology of motivation to improve customer and employee engagement. Examples include: incentive systems, training programs, customer loyalty and reward programs and online engagement platforms. Gamification has proven to be very successful in engaging people and motivating them to change behaviors, develop skills or solve problems.
Click on the examples below to enlarge
Applications
Serious Games
Games designed for tutorial training and simulating, for practicing and for knowledge learning and different scenarios simulations.
Students become players and interact to develop and to learn tutorial contents.
Interactions through digital means augmenting theory and practice concepts to users.
Games designed to develop technical and emotional skills.
Generating environments and training users to obtain experience through challenges
Games and applications which contribute to analyze applicants’ profiles, to test skills and to check their knowledge.
Gamification
Application of game elements in several environments seeking a business objective through entertaining.
Dynamic Integrations and platforms for integrating people and groups with mutual interests
Game elements changing the usual design and esthetics formats creating a game-like environment in the real world.
Day-to-day situations redesigned to promote civic and social conducts through games.
Scoring platforms, challenges and information sharing to stimulate the practice of sports.
Scoring platforms, challenges and information sharing to stimulate the practice of sports
Company platforms using game elements to engage employees in internal incentive campaigns
“Gamification is the concept which gathers the use of mechanics, dynamics and game tools in “non-games” contexts seeking to further engage people more efficiently in processes.”gamification.org
Gamification Concept
Gamification is a recent area of knowledge which seeks to structure, to define and to apply best practices and techniques which bring a fascinating and complex reality of games to real life contexts both under the light of education as well as of all business branches.
This trend concentrates on the human element, on people and their senses where a process/system is either designed or re-defined using game elements and mechanics to maximize customers’ behavior such as engagement, interest, entertainment, attention, loyalty and several other behaviors aligned to a business objective or educational strategies. As far as the educational field is concerned, a concept called Serious Games is generated ranging from the application of simulations which re-create an environment/ equipment in order to train players until games based on specific knowledge areas to help develop and learn contents (some examples in the educational field are given below)
Defined in 2002 by Nick Pelling, the term Gamification has taken shape as from 2010 when the possibilities connected to the study and application of this technique called the attention of the private sector mainly represented by a group of investors from the Silicon Valley area in California.

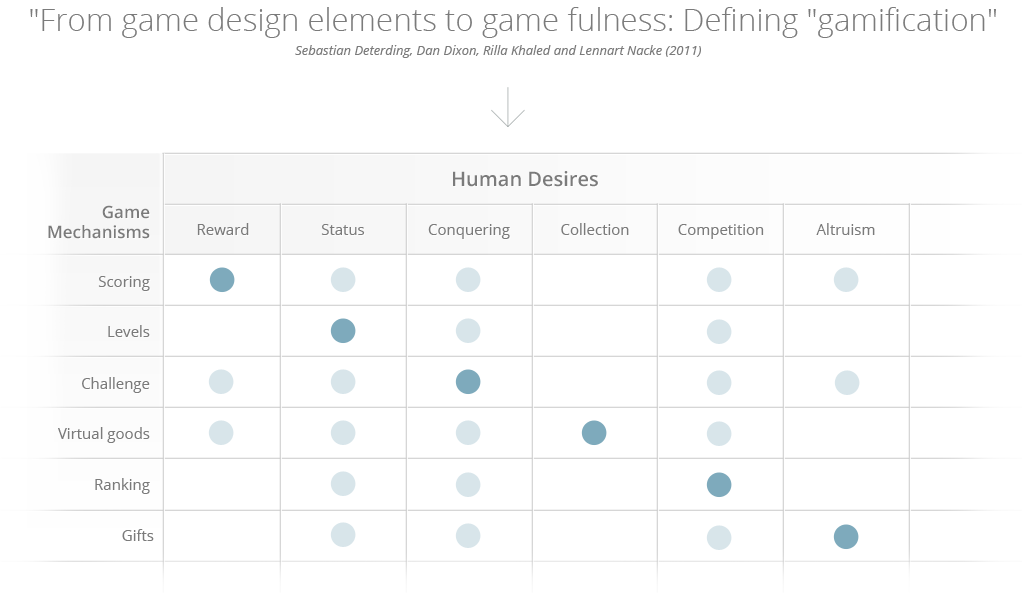

Study centers begin to arise, both in the private and academic sectors, which develop into startups and reference groups where the foundation of this science has been structured and tested already under an extremely practical point of view and focused on corporate problem solving. Good practices and successful cases have extensively been discussed and applied around the world (many of such examples are found in this website session).
In the Brazilian Market, this sector is still quite undeveloped and it is generally observed in companies whose core business has some corresponding areas such as marketing, game design, information/web business among others and add up this subject to their product portfolio or services as a distinguishing factor. However, in most cases, companies still lack expertise. Likewise the private sector, Brazilian educational institutions are still timidly learning about Gamification or Serious Games. In some schools, especially colleges, we can find this subject being worked on separately or as part of corresponding subjects such as advertising, social media and strategic marketing to mention a few.
Although this is a promising new way to face the business and education world, some unsuccessful cases have been detected due to the lack of planning and knowledge from adventurers leading to frustration and financial losses when applying game elements to real processes without due know-how.

Serious Game Concept
In Brazil, the application of games in the correlated areas mentioned above took place in the educational sector although in a limited, moderate way. A recent example is the Federal University of Goiás where a game was developed by Genetics professors and applied to students who had low learning performance on specific chapters which involved complex chromosome operations. Professors were stimulated to find an alternative way to traditional methods by developing a board game which taught the concepts in a playful way generating positive learning results.
“Among the ten participating courses in this pilot game, professors confirmed a 44% average increase of right answers for 6 genetics questions worked on this board game.”
For this action, undergraduate students in their freshman year who had genetics in their curriculum were submitted to a pre-test (measuring effectiveness of lectures) and later on submitted to a new test after the application of the game (post-test).
Supported by these case results, nowadays there is strong evidence, both in theory and practice, of how successful the use of game-based pedagogical models are for a more effective learning. Other applications classified as Serious Games are: simulators, company games, e-learning platforms, recruitment and selection dynamics, games in internal enterprise portals among other examples mentioned in this session.

Here are some successful cases of gamification and serious games.
Some website references, books and articles about gamification.

